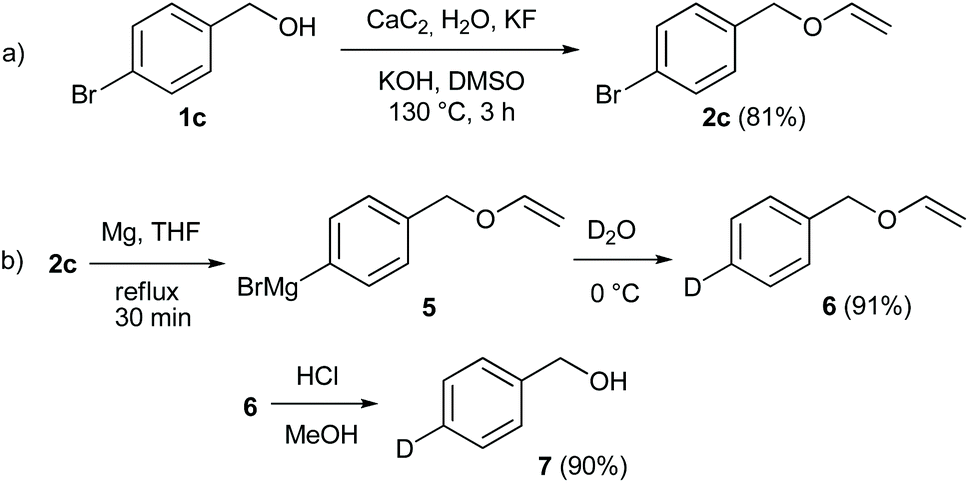
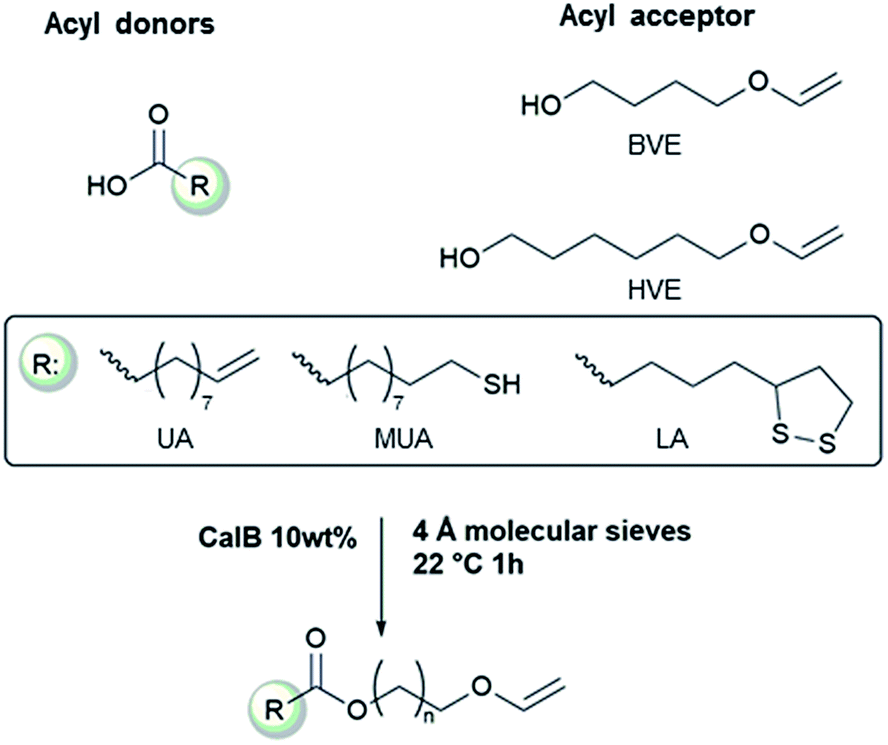
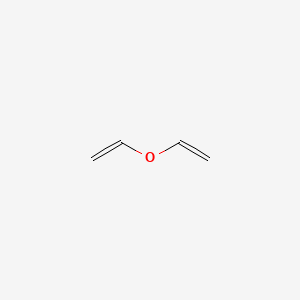
During efforts to employ a claisen rearrangement in the synthesis of a complex nucleoside a highly functionalized protected vinyl ether was required as a key intermediate.
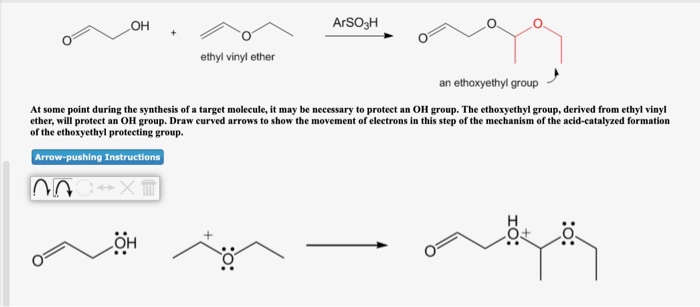
Vinyl ether protecting group.
The acetal is then called a protecting group for the carbonyl.
This step is called deprotection.
1 when a propionaldehyde derived super silyl enol ether was used syn selectivity was observed scheme 1 table 1.
The super silyl group allows for the construction of β hydroxy aldehydes for a broad range of aldehydes providing 1 1 adducts in high yield.
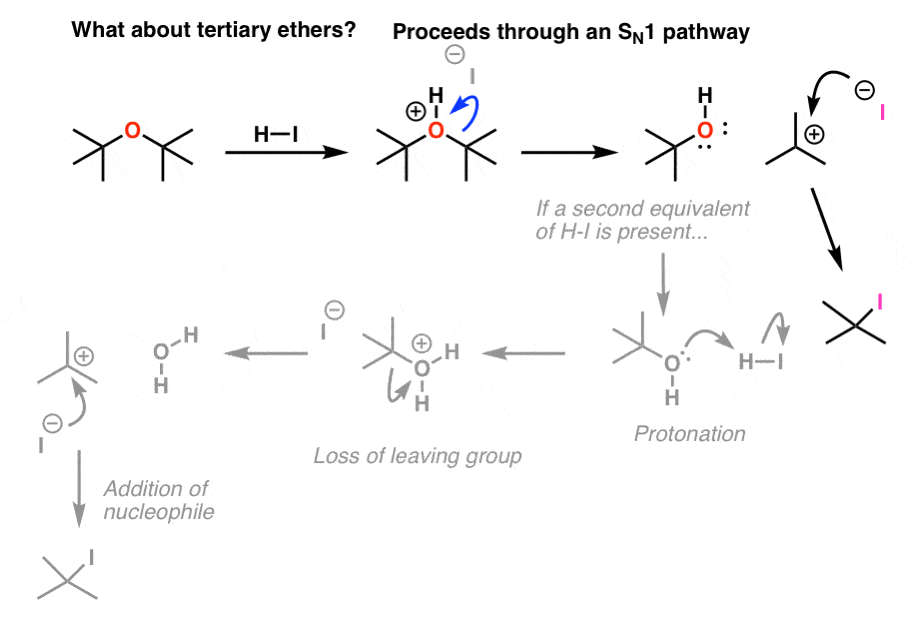
The optimal route to this vinyl ether was found to be a remarkably selective ring opening of a cyclic acetal with tmsotf and net 3.
A readily recyclable fluorous alkoxy ethyl ether protecting group has been developed that allows for simple purification of small to medium sized organic molecules by liquid liquid extraction with fc 72 organic aqueous solvents.
After the step involving the hydride is complete the acetal is removed by reacting it with an aqueous acid giving back the original carbonyl.
The step to form the protected intermediate and a deprotection once the.
Isomerization to the more labile enol ether employing ko t bu with subsequent mild acidic hydrolysis is one of the most common deprotection methods.
Etoch ch 2 roh etoch or ch 3.
Ethyl vinyl ether participates in many reactions of interest to organic synthesis.
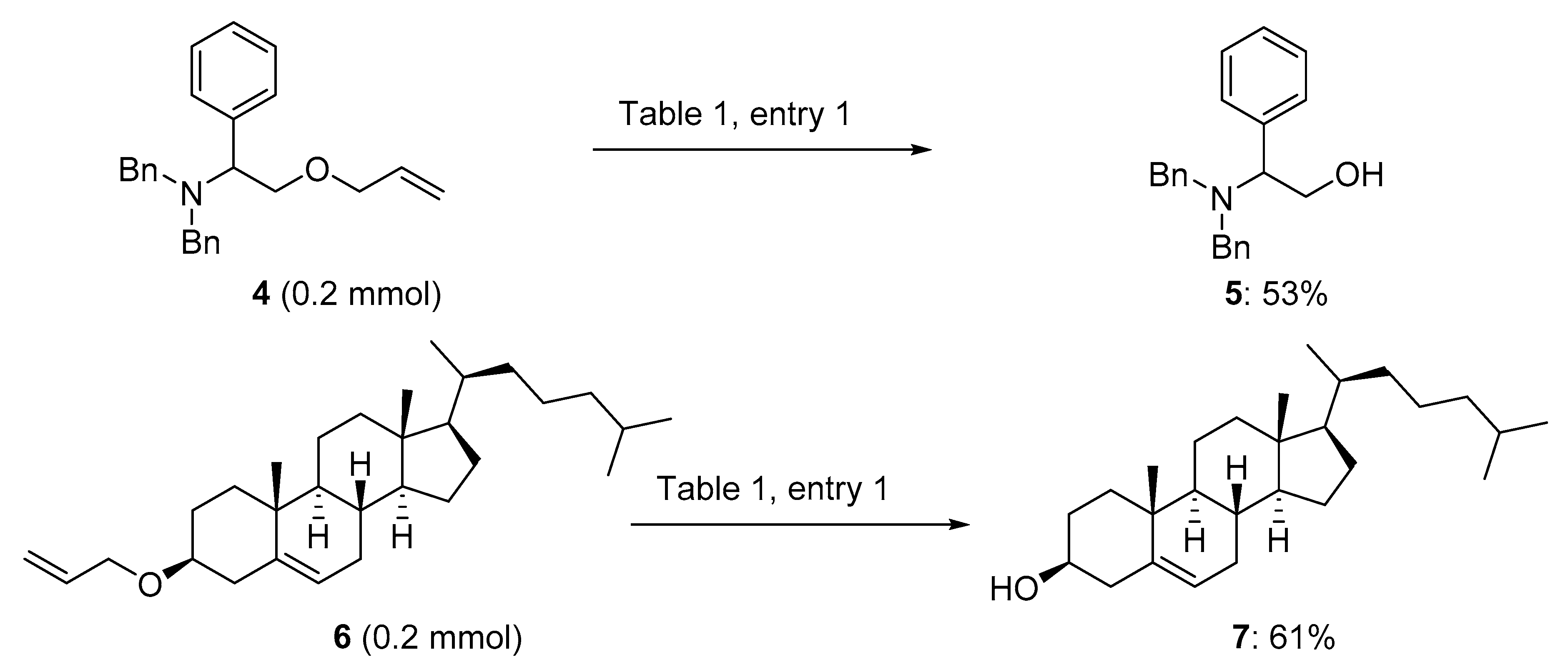
The allyl group is a commonly used protecting group for alcohols with relative stability towards both acidic and basic conditions that permits orthogonal protection strategies.
Silyl ethers are a group of chemical compounds which contain a silicon atom covalently bonded to an alkoxy group.
Protecting an amine as a carbamate therefore enables other functional groups to undergo selective reactions with electrophiles whereby the carbamate protected amino group is left intact.
However two additional synthetic steps are needed to achieve this protection.
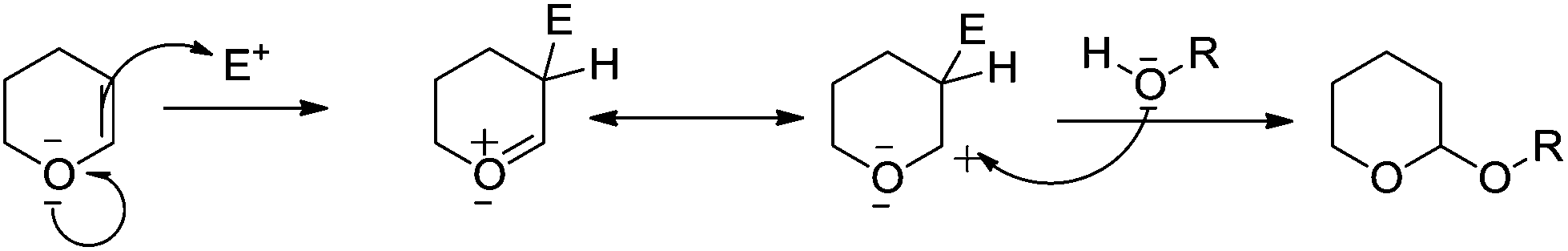
This alcohol protection reaction is akin to the behavior of dihydropyran.
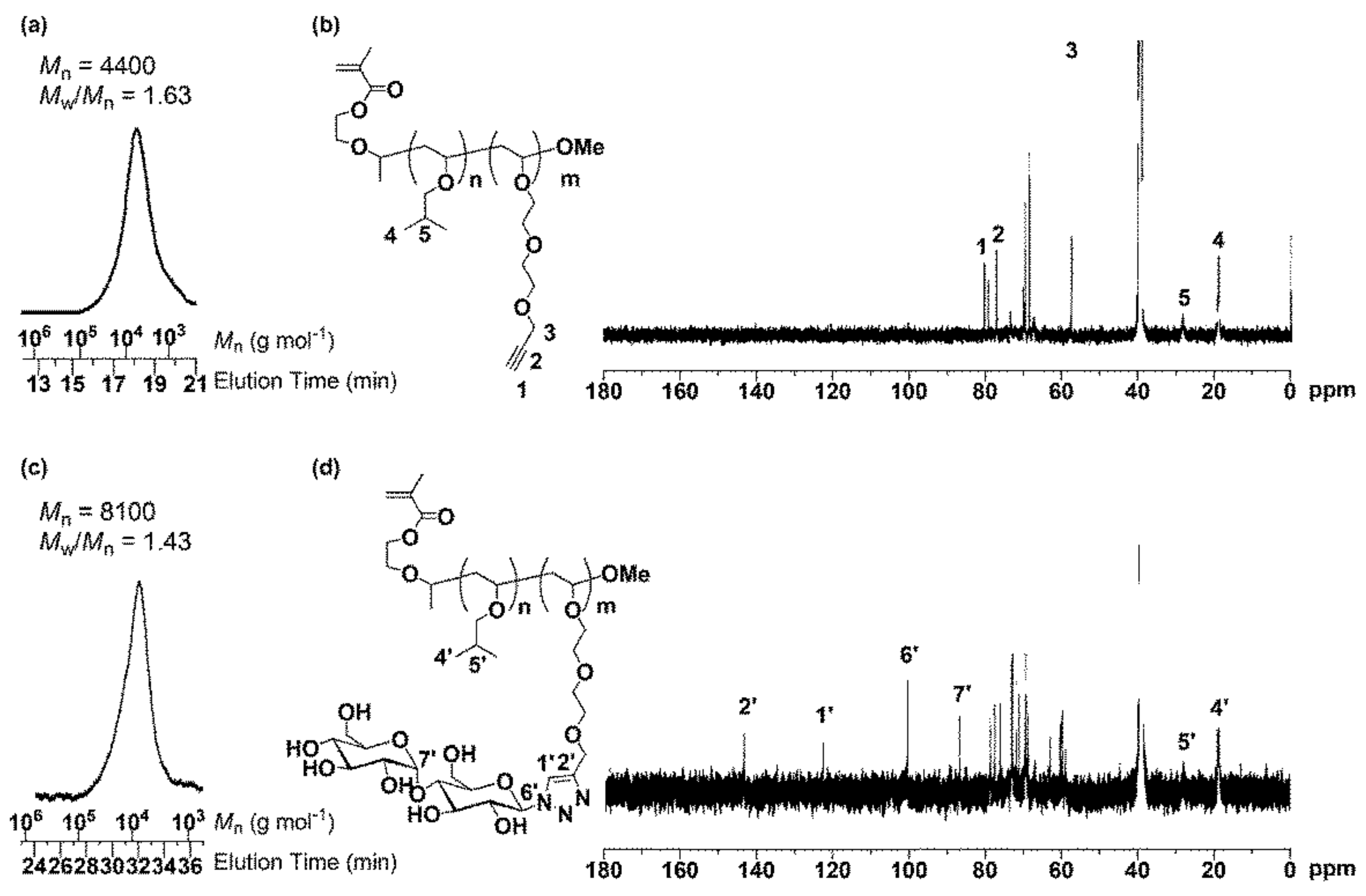
The polymers formed have a ketone end group e g 19 scheme 9 functionality can be introduced on z or r to modify reactivity or to tailor the end groups as in the examples 20 22.
21 the vinyl ether transfer agents like other vinyl ethers generally show marked acid sensitivity and are not suited for use with acidic monomers e g acrylic acid aa methacrylic acid maa.
The general structure is r 1 r 2 r 3 si o r 4 where r 4 is an alkyl group or an aryl group.